Do you know what's on your network? In this guide, we'll show you a few simple ways you can find an IP address on your network. We'll also go over a few great tools that can speed up this process and give you further insight into your network.
Whether you're managing an office network, or just doing some troubleshooting at home, knowing how to find a device's IP address is critical in solving a number of networking problems.
Avoid using routers supplied by ISPs. These routers are typically less secure than those sold. Every device on a home network must be uniquely identified with an IP (Internet Protocol) address. An IP address consists of four sets of numbers from 0 to 255, separated by a decimal, such as: 192.168.1.200 Although the numbers in an IP address may appear random, there is a method to the madness. If you're using Windows, you can find your router's IP address by using the Command Prompt app or the Control Panel. From the Command Prompt app, type ipconfig, hit Enter, and your system will bring up your default gateway or IP address. In Control Panel, go to Network and internet View network status and tasks Ethernet Details. IP Address stands for Internet Protocol Address and all devices on the network have an IP Address assigned to it. So, what is my ip address? An IP address is made up of 4 numbers in the following format: aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd. Each number can be in the range of 0-255. An IP address is defined as 'a numerical label assigned to each devices (e.g.
Let's start with the most basic method of finding your own local IP address in two easy steps.
- Open a command line window. In Windows, you can do this by pressing Windows Key + R, and then typing cmd in the Run box and hitting enter. In Linux, this can be done by pressing Ctrl+Alt+T.
- Type ipconfig in the command line if you're on Windows, and ifconfig if you're on Linux. Press enter to get a list of your PC's IP configuration.
In the command prompt, you'll find your IPv4 address towards the top. Under it, you'll see your subnet mask and your default gateway. This information is vital, especially if you're having issues connecting to the internet.
But what about finding other IP addresses that might be on your network?
To find other IP addresses that are on your local network, type arp -a in the same command prompt window and press enter. A list of IP addresses will populate on your screen along with additional information you might find helpful.
IP Addresses
In the far left-hand column you'll see a list of IP addresses that were discovered on your network. Towards the bottom of the list, you may see some addresses starting with 224, 239, or 255. These addresses are generally reserved by your router for administrative purposes, so these can be looked over.
Physical Addresses
In the second column under Physical Addresses we'll see each device's physical address. This is also commonly referred to as a MAC address. A physical address is a unique identifier that every network device comes with. Unlike IP addresses, this number cannot be changed. Knowing a device's physical address is important, especially if you want to identify exactly what is on your network.
Type
The last column displays the address's type. There are two types of IP addresses, dynamic and static. A dynamic address means that a DHCP server gave that device an IP address. A static address means that the device was configured to use a specific IP address, one that won't change.
Static addresses are great for devices that are permanent, like printers or servers. Most home networks will be fine using DHCP to hand out IP addresses. DHCP servers assign IP addresses that have leases. Once that lease is up, that device might get a different IP address.
Troubleshooting
From your command prompt, you're a bit limited in how you can interact with devices on the network. You can attempt to ping an IP address on your network by typing ping 192.168.XX.XXX (Replace the X's with your IP address.)
Most devices will answer the ping and reply back. This is a quick and easy way to determine if there are any latency issues between your PC and that device. For further troubleshooting, we're going to need to use some network analyzer tools.

These tools are great for quickly finding devices on your local network and spotting problems fast. They also provide a lot more details than your trusty old command prompt can give you.
Below are three of my favorite network scanning programs.
SolarWinds Port Scanner (FREE TOOL)
If you need more detail and functionality from your Port Scanner then SolarWinds has you covered. You can easily scan your network by IP ranges and filter by ports to identify what services a device is running. SolarWinds Port Scanner is currently a Windows tool only.
SolarWinds Port Scanner also automatically resolves hostnames to help you identify what devices are on your network faster. The GUI interface is easy to use and boasts a cleaner display than Angry IP Scanner.
For those who live in the command line, you'll be glad to hear this tool comes with a fully functional CLI and support for batch scripting.
While these tools are great, they won't proactively alert you to problems on your network such as duplicate IP addresses, or DHCP exhaustion.
My Home Upcoming
If you're a small business administrator, or just a curious tech looking for a bit more insight into your network, SolarWinds Port Scanner is an excellent tool and is available as a free download.
Paessler PRTG Network Scanning Tools (FREE TRIAL)
If you're a network administrator like myself, you'll find PRTG Network Monitor an extremely valuable tool when it comes to troubleshooting problems across your network. PRTG is really the evolution of a scanning tool and more of a complete network monitor.
My Home Ipad
PRTG first scans the entire network in its network discovery process, listing any devices it can find. Once the scan is complete it keeps a real-time inventory of all devices and records when any are removed or added.
PRTG's sensors are perfect for in-depth testing across your networks. Ping sensors can easily monitor a device's connectivity over the long term, and alert you to those intermittent connection problems that can be difficult to pin down.
The PRTG scanner goes a step further by also incorporating database monitoring into its suite of tools. This sensor will alert you to any outages or long wait times in almost any SQL environment. Database monitoring can help identify small problems such as stalled processes before they cause major downtime.
Lastly, PRTG can thoroughly monitor bandwidth and network utilization for your environment. When things slow to a crawl, you'll be able to quickly identify which IP addresses are using the most bandwidth and pinpoint exactly what that traffic is.
Is someone streaming too much Netflix? With the usage monitoring sensor, you'll never have to guess what is hogging up your bandwidth again. This data is beautifully displayed as a chart, and broken down by IP address, protocol, or top connections.
When you have a sample of data you'd like to save, you can easily export it to XML or CSV. You can even tap into the PRTG API and export your data in real-time.
PRTG is a powerful on-premise tool and is geared mostly for medium to large businesses. It installs in a Windows server environment and gives you full control of what sensors you'd like to activate. If you'd like to test it out yourself you can download a 30-day free trial.
Angry IP Scanner
One of my favorite free tools is the Angry IP Scanner. It's compatible with Mac, Linux, and Windows and allows you to quickly find detailed information about devices that are on your network.
Simply select an IP range at the top and let Angry IP Scanner work its magic. Almost instantly Angry IP will begin pulling information about the IP range you specified.
At a glance you'll be able to see what IP addresses are open for assignment, taken by devices, and how many ports each device has open.
If you're having trouble finding a device on your network, Angry IP Scanner makes it simple to track down that device for further troubleshooting.
Angry IP Scanner has personally helped me find devices that have lost their static IP address without having to physically go to the device.
If you're looking to export and save your findings, you can easily download your results in CSV, XML, or text format. It is available as a free download.
Final Thoughts
No matter what size network you're troubleshooting, understanding how to find a device's IP address is essential.
Whether you're quickly looking up the ARP table with the arp -a command, or utilizing a network tool like PRTG, having a solid grasp of what's on your network will help keep all of your device safe, and yourself headache free.
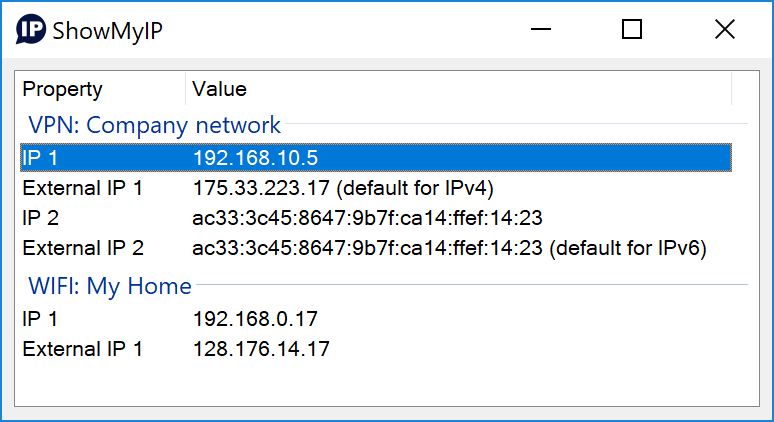
Although you may not know it, but you have two IP addresses, an Internal IP address (Private ) and an external IP address (Public).
Why do you need two IP addresses and what is the difference between an Internal and external IP address?
What Is an External IP Address?
The external IP address or Public IP address is the IP address of the router interface that is connected to the Internet.
Here is a diagram to illustrate the IP address allocation on a typical home or small business network.
A router will typically have two network interfaces.
- An Internal Interface
- An external Interface
Each of these interfaces will have an IP address. The IP address assigned to the external Interface will have a routable IP address and will be assigned by your ISP.
This address is also known as the public address.
Public address ranges are assigned to ISPs by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA.
On Home office networks that use a NAT router the internal IP addresses use a special IP address range.
My Home Iphone App
This address range is specifically reserved for internal addresses and the IP addresses will not be forwarded by routers on the Internet.
Internal Addresses are also called Private addresses as they are restricted to private networks.
All of the devices on my home network have addresses like 192.168.1.x but externally they have the address 109.155.209.167
Home networks usually use addresses in the .192.168.0.* or .192.168.1.* address range.
The 192.168.0.0 network address range is a designated non route-ableprivate network address.
However they are not the only non route-able private address ranges that you can use. Others address ranges that can be used are:
- 10.x.x.x is a 24 bit address block
- 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x is a 20 bit address block.
See wiki private networks for more details
Note: You may want to read the IP4 Addresses and classes tutorial if you are unfamiliar with network addresses.
Finding Your External (Public) and Internal (Private) IP Addresses

To find your external IP address do a search for your IP address in Google then you will probably see a screen like this
Google shows an IP address:
109.155.209.167
This is your external IP address.
Now open a command line and type:
ipconfig
You should see something like this:
This time your IP address is 192.168.1.64
This is your Internal IP address.
The internal IP address, is used on your local internal network and the external IP address is used when communicating with machines on the Internet.
Allowing Access from The Internet To Your Network
Because of the NAT router there is no direct connection between the Internet, and a computer on the local network. Dlna universal media server.
All communication between your Internal network and the Internet must be initiated by a device on your Internal network.
Generally this isn't a problem, and is a security advantage.
However online gamers, and those who would like to host a website or other services on their own network will need to allow external devices on the Internet to access them.
To accomplish this NAT routers can be configured to use a technique called port forwarding.
Port forwarding allows an internal device to to appear to have an external IP address, and allows incoming connections from the Internet.
Summary
Home and business networks use private or internal addresses from a reserved non route-able address range.
On Home and Small Office networks a NAT router connects the internal network to the Internet using a single route-able external or public IP address assigned by the ISP from it's allocated address block.
The NAT router allows connections to be established only from the internal network to the external network and not vice-versa unless techniques like port forwarding are employed.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- My External IP Address Keeps Changing. Is this normal? Can I stop it?
A- Most ISPs will allocate dynamic IP addresses to their customers. This Address will become the External IP address assigned to your router, and hence it could change.
This is a screenshot showing how my own external IP address has changed over a month.
Some ISPs will allow you to have a static IP address but usually at a premium ( Business broadband)
Static IP addresses do not change.
If you intend providing access to your network from the Internet, then you really need a static external IP address.
However an alternative for home and small business networks is to use a dynamic DNS service.
A dynamic DNS service doesn't stop the external address from changing, but instead it tracks these changes automatically and updates the DNS records automatically when the IP address changes.
Video
For those who prefer video then I've create a video on YouTube that covers the main points above.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- Can You Use an internal IP address on the Internet?
A-No – The internal IP address ranges discussed above are blocked by Internet routers.
Q- How does a message reach an Internal IP Address from an external one?
A- This is done using a translation table on the NAT router, and is covered in understanding port forwarding.
Q- Does in make any difference if I use the 10. IP address range and not the 192.168.0.0 address range.
A –No none at all. However most home routers are preset to use the 192.168 address range.
Q- Who assigns my external IP (Public) address?
A- It is assigned by your ISP.
Q- How do I know if my External Address has changed?
My Computer Ip Address Windows 10

From your command prompt, you're a bit limited in how you can interact with devices on the network. You can attempt to ping an IP address on your network by typing ping 192.168.XX.XXX (Replace the X's with your IP address.)
Most devices will answer the ping and reply back. This is a quick and easy way to determine if there are any latency issues between your PC and that device. For further troubleshooting, we're going to need to use some network analyzer tools.
These tools are great for quickly finding devices on your local network and spotting problems fast. They also provide a lot more details than your trusty old command prompt can give you.
Below are three of my favorite network scanning programs.
SolarWinds Port Scanner (FREE TOOL)
If you need more detail and functionality from your Port Scanner then SolarWinds has you covered. You can easily scan your network by IP ranges and filter by ports to identify what services a device is running. SolarWinds Port Scanner is currently a Windows tool only.
SolarWinds Port Scanner also automatically resolves hostnames to help you identify what devices are on your network faster. The GUI interface is easy to use and boasts a cleaner display than Angry IP Scanner.
For those who live in the command line, you'll be glad to hear this tool comes with a fully functional CLI and support for batch scripting.
While these tools are great, they won't proactively alert you to problems on your network such as duplicate IP addresses, or DHCP exhaustion.
My Home Upcoming
If you're a small business administrator, or just a curious tech looking for a bit more insight into your network, SolarWinds Port Scanner is an excellent tool and is available as a free download.
Paessler PRTG Network Scanning Tools (FREE TRIAL)
If you're a network administrator like myself, you'll find PRTG Network Monitor an extremely valuable tool when it comes to troubleshooting problems across your network. PRTG is really the evolution of a scanning tool and more of a complete network monitor.
My Home Ipad
PRTG first scans the entire network in its network discovery process, listing any devices it can find. Once the scan is complete it keeps a real-time inventory of all devices and records when any are removed or added.
PRTG's sensors are perfect for in-depth testing across your networks. Ping sensors can easily monitor a device's connectivity over the long term, and alert you to those intermittent connection problems that can be difficult to pin down.
The PRTG scanner goes a step further by also incorporating database monitoring into its suite of tools. This sensor will alert you to any outages or long wait times in almost any SQL environment. Database monitoring can help identify small problems such as stalled processes before they cause major downtime.
Lastly, PRTG can thoroughly monitor bandwidth and network utilization for your environment. When things slow to a crawl, you'll be able to quickly identify which IP addresses are using the most bandwidth and pinpoint exactly what that traffic is.
Is someone streaming too much Netflix? With the usage monitoring sensor, you'll never have to guess what is hogging up your bandwidth again. This data is beautifully displayed as a chart, and broken down by IP address, protocol, or top connections.
When you have a sample of data you'd like to save, you can easily export it to XML or CSV. You can even tap into the PRTG API and export your data in real-time.
PRTG is a powerful on-premise tool and is geared mostly for medium to large businesses. It installs in a Windows server environment and gives you full control of what sensors you'd like to activate. If you'd like to test it out yourself you can download a 30-day free trial.
Angry IP Scanner
One of my favorite free tools is the Angry IP Scanner. It's compatible with Mac, Linux, and Windows and allows you to quickly find detailed information about devices that are on your network.
Simply select an IP range at the top and let Angry IP Scanner work its magic. Almost instantly Angry IP will begin pulling information about the IP range you specified.
At a glance you'll be able to see what IP addresses are open for assignment, taken by devices, and how many ports each device has open.
If you're having trouble finding a device on your network, Angry IP Scanner makes it simple to track down that device for further troubleshooting.
Angry IP Scanner has personally helped me find devices that have lost their static IP address without having to physically go to the device.
If you're looking to export and save your findings, you can easily download your results in CSV, XML, or text format. It is available as a free download.
Final Thoughts
No matter what size network you're troubleshooting, understanding how to find a device's IP address is essential.
Whether you're quickly looking up the ARP table with the arp -a command, or utilizing a network tool like PRTG, having a solid grasp of what's on your network will help keep all of your device safe, and yourself headache free.
Although you may not know it, but you have two IP addresses, an Internal IP address (Private ) and an external IP address (Public).
Why do you need two IP addresses and what is the difference between an Internal and external IP address?
What Is an External IP Address?
The external IP address or Public IP address is the IP address of the router interface that is connected to the Internet.
Here is a diagram to illustrate the IP address allocation on a typical home or small business network.
A router will typically have two network interfaces.
- An Internal Interface
- An external Interface
Each of these interfaces will have an IP address. The IP address assigned to the external Interface will have a routable IP address and will be assigned by your ISP.
This address is also known as the public address.
Public address ranges are assigned to ISPs by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA.
On Home office networks that use a NAT router the internal IP addresses use a special IP address range.
My Home Iphone App
This address range is specifically reserved for internal addresses and the IP addresses will not be forwarded by routers on the Internet.
Internal Addresses are also called Private addresses as they are restricted to private networks.
All of the devices on my home network have addresses like 192.168.1.x but externally they have the address 109.155.209.167
Home networks usually use addresses in the .192.168.0.* or .192.168.1.* address range.
The 192.168.0.0 network address range is a designated non route-ableprivate network address.
However they are not the only non route-able private address ranges that you can use. Others address ranges that can be used are:
- 10.x.x.x is a 24 bit address block
- 172.16.x.x to 172.31.x.x is a 20 bit address block.
See wiki private networks for more details
Note: You may want to read the IP4 Addresses and classes tutorial if you are unfamiliar with network addresses.
Finding Your External (Public) and Internal (Private) IP Addresses
To find your external IP address do a search for your IP address in Google then you will probably see a screen like this
Google shows an IP address:
109.155.209.167
This is your external IP address.
Now open a command line and type:
ipconfig
You should see something like this:
This time your IP address is 192.168.1.64
This is your Internal IP address.
The internal IP address, is used on your local internal network and the external IP address is used when communicating with machines on the Internet.
Allowing Access from The Internet To Your Network
Because of the NAT router there is no direct connection between the Internet, and a computer on the local network. Dlna universal media server.
All communication between your Internal network and the Internet must be initiated by a device on your Internal network.
Generally this isn't a problem, and is a security advantage.
However online gamers, and those who would like to host a website or other services on their own network will need to allow external devices on the Internet to access them.
To accomplish this NAT routers can be configured to use a technique called port forwarding.
Port forwarding allows an internal device to to appear to have an external IP address, and allows incoming connections from the Internet.
Summary
Home and business networks use private or internal addresses from a reserved non route-able address range.
On Home and Small Office networks a NAT router connects the internal network to the Internet using a single route-able external or public IP address assigned by the ISP from it's allocated address block.
The NAT router allows connections to be established only from the internal network to the external network and not vice-versa unless techniques like port forwarding are employed.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- My External IP Address Keeps Changing. Is this normal? Can I stop it?
A- Most ISPs will allocate dynamic IP addresses to their customers. This Address will become the External IP address assigned to your router, and hence it could change.
This is a screenshot showing how my own external IP address has changed over a month.
Some ISPs will allow you to have a static IP address but usually at a premium ( Business broadband)
Static IP addresses do not change.
If you intend providing access to your network from the Internet, then you really need a static external IP address.
However an alternative for home and small business networks is to use a dynamic DNS service.
A dynamic DNS service doesn't stop the external address from changing, but instead it tracks these changes automatically and updates the DNS records automatically when the IP address changes.
Video
For those who prefer video then I've create a video on YouTube that covers the main points above.
Common Questions and Answers
Q- Can You Use an internal IP address on the Internet?
A-No – The internal IP address ranges discussed above are blocked by Internet routers.
Q- How does a message reach an Internal IP Address from an external one?
A- This is done using a translation table on the NAT router, and is covered in understanding port forwarding.
Q- Does in make any difference if I use the 10. IP address range and not the 192.168.0.0 address range.
A –No none at all. However most home routers are preset to use the 192.168 address range.
Q- Who assigns my external IP (Public) address?
A- It is assigned by your ISP.
Q- How do I know if my External Address has changed?
My Computer Ip Address Windows 10
My Home Iphone Accessories
A- You will need to check it using the technique shown earlier.
Q- Can I change my External IP Address?
A- No
Related Articles and Resources:

